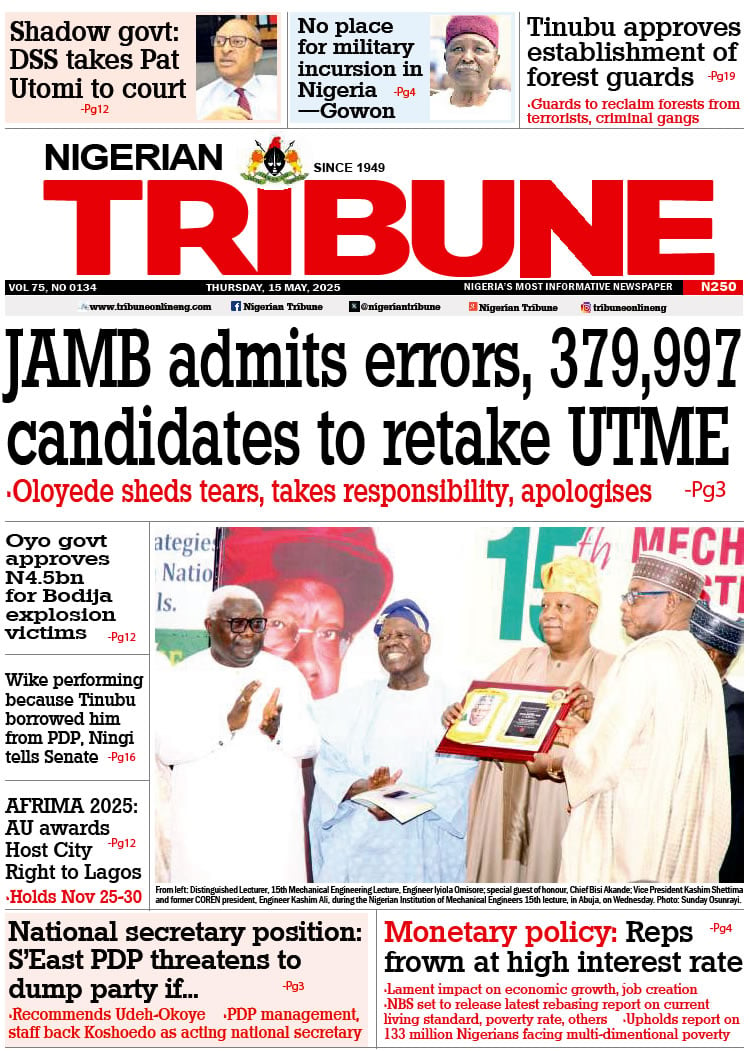
Leveraging vision, policy and knowledge for sustainable practices.
Entrepreneurship is what many scholars consider as one of the factors responsible for nation-building. While innovation involves introducing something new, such as a business model, product, idea, or service, entrepreneurship focuses on turning a great idea into a viable business opportunity. Innovation is the starting point for entrepreneurship, as it involves the creation of new and valuable ideas. Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services.
Innovation drives progress, propelling businesses and societies forward. It is the lifeblood of entrepreneurship and economic growth, improving efficiency, and enhancing our quality of life. From groundbreaking technologies to revolutionary business models, innovation shapes the world around us.
Innovation enhances the quality of life by introducing new products and services that address human needs and wants. It leads to advancements in healthcare, education, transportation, and communication, making daily tasks easier and more efficient. Examples include:
- Medical innovations like gene therapy and personalized medicine
- Smart home technologies that automate household tasks
- E-learning platforms that make education more accessible and flexible
- Renewable energy technologies like solar panels and wind turbines
- Water purification systems for areas with limited access to clean water
- Artificial intelligence applications in climate modeling and prediction
In spite of being considered an undisputed engine of growth, innovation can have noxious consequences for society and the environment. While innovation drives progress, it also brings potential risks that require careful consideration. These risks can impact various aspects of society, business, and individual lives. The rapid and uncontrolled proliferation of innovations in industries is a manifestation of “entrepreneurial cancer”. For instance, AI experts warn that advanced chatbots like GPT-4 may soon reach artificial general intelligence (AGI) and outsmart humans. They argue that we need to regulate AI development and avoid a nuclear-level catastrophe.
Entrepreneurship is supposed to bring development to societies and economies. Vision is the direction of development. Development is based on innovative ideas and visionary agendas of entrepreneurs and governments, respectively. Creativity for the sake of creativity is the ideology of “entrepreneurial cancer.” Sustainable social, economic and environmental development goals are hinged on vision. Vision is essentially about the direction of development or the development of direction for social, economic and environmental goals. Either ways, the ideology of a nation is a function of its entrepreneurial formulas as well as policy formulation.
“Growth for the sake of growth is the ideology of the cancer cell.” – Edward Abbey
“Innovation is the specific tool of entrepreneurs who exploit change as an opportunity for a different business or service.” – Peter Drucker
What innovation is to entrepreneurship is what policy is to governance.
Policy is a regulator of innovation, it is the specific tool of governments and organisations.
Sustainable development goes beyond the generation of the best entrepreneurial ideas, it is about leaving the best ideas for the next generation of entrepreneurs.
Policy can be defined as a course or principle of action adopted or proposed by an organization or individual. Policy is a deliberate system of guidelines to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent and is implemented as a procedure or protocol. Policies are generally adopted by a governance body within an organisation.
Policy is a regulator of entrepreneurial initiatives or innovative activities. Without regulation, innovation, that is, the application of creative solutions to problems and to opportunities to enhance and to enrich people’s lives, may lead to a complication.
Innovation Policy refers to a set of policy actions aimed at enhancing the quantity and efficiency of innovative activities, which involve creating, adapting, and adopting new or improved products, processes, or services. These policies are crucial for fostering technology, knowledge, and skills transfer among industries, science, and technology organisations at local, regional, and national levels.
Responsible innovation practices and adaptive regulatory frameworks are crucial for balancing the benefits and risks of innovations. Responsible innovation practices prioritize ethical considerations and long-term societal impacts. These practices include:
- Stakeholder engagement: Involving diverse groups in the innovation process
- Impact assessments: Evaluating potential consequences before implementation e.g., Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
- Transparency: Openly communicating research methods and findings
- Sustainable design: Incorporating eco-friendly principles into product development
- Ethical guidelines: Establishing clear protocols for emerging technologies
Implementing these practices helps mitigate risks while maximizing innovation benefits. Companies that adopt responsible innovation strategies often experience improved public trust and long-term sustainability.
Regulatory Frameworks
Research has shown that government policies and regulations can promote or hinder innovation. Regulatory frameworks provide essential guidelines for managing innovation risks without stifling progress. Key aspects of effective regulatory frameworks include:
- Adaptive governance: Flexible policies that evolve with technological advancements
- International cooperation: Harmonized standards across borders to address global challenges
- Risk-based approach: Tailoring regulations to the level of potential harm
- Sandboxing: Controlled environments for testing innovative products or services
- Public-private partnerships: Collaboration between government and industry for balanced oversight
Regulatory frameworks create a level playing field for innovators while protecting public interests. They establish clear boundaries for ethical innovation and help prevent unintended negative consequences.
Governments can foster innovation in several ways:
- By buying innovation, i.e. by being the lead customer
- By reducing the risk of innovation
- By collaborating on innovation
- By using standards or regulations to encourage innovation
- By ensuring the underlying infrastructure exists for both large and small businesses to build upon
“Growth for the sake of growth is the ideology of the cancer cell.” – Edward Abbey
“Innovation is the specific tool of entrepreneurs who exploit change as an opportunity for a different business or service.” – Peter Drucker
What innovation is to entrepreneurship is what knowledge is to research and development (R&D).
Knowledge is a regulator of innovation, it is the specific tool of academics and researchers.
The best way to predict the future is to invest in R&D.
“The calculus of innovation is really quite simple: Knowledge drives innovation, innovation drives productivity, productivity drives economic growth.” – William Brody
“When you know better, do better”. – Maya Angelou.
“Learning and innovation go hand in hand. The arrogance of success is to think that what you did yesterday will be sufficient for tomorrow.” – William Pollard
READ ALSO: